-
Products
- Gas analysis systems
- GAOS SENSON gas analyzers
- GAOS MS process mass spectrometry
- MaOS HiSpec ion mobility spectrometer
- MaOS AxiSpec ion mobility spectrometer
- Applications
- News
- Events
- About us
 |
|
|
|
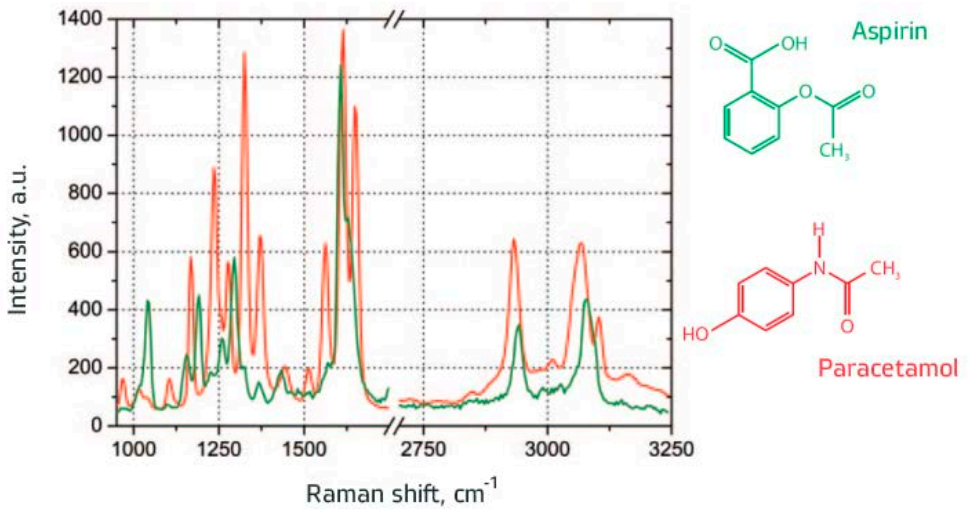 |
The characteristic spectra of aspirin and paracetamol. The Raman spectrum of paracetamol has characteristic peaks near 1650 cm-1 (C = O stretching vibration) and 1612 cm-1 (N-H stretching vibration). The Raman spectrum of aspirin has characteristic bands of 1606 cm-1 (C-C stretching vibration) and 1622 cm-1 (C-O vibration of carboxyl group). |
|
|
Laser 532 nm * |
Laser 785 nm * |
||
|
Laser power |
50 mW
|
130 mW |
||
|
Laser attenuation |
1-100% with 1% step |
|||
|
Focal length |
120 mm |
|||
|
Entrance aperture |
40 µm |
|||
| Grating |
1200 l/mm |
1800 l/mm |
600 l/mm |
1200 l/mm |
|
Spectral resolution |
~7 cm-1 |
~4 cm-1
|
~7 cm-1 |
~3 cm-1 |
|
Spectral range |
|
|||
|
- Edge/Notch filter
|
70 – 4 700 cm-1 |
70 – 3 155 cm-1 |
50 – 3 200 cm-1 |
50 – 2 140 cm-1 |
|
- Bragg filter |
10 – 4 700 cm-1 |
10 – 3 155 cm-1 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Detector |
||||
|
Detector type |
sCMOS |
|||
|
Pixel number |
4 096 |
|||
|
Pixel size |
7 x 200 µm |
|||
|
Readout noise |
16 e rms |
|||
|
Dark current |
400 e-/pixel/s |
|||
|
Dynamic range |
5 000:1 |
|||
|
Peak sensitivity wavelength |
700 nm |
|||
|
Integration time |
1 ms – 60 s |
|||
| PC connection interface |
USB 2.0 |
|||
|
Power supply |
100 – 240 VAC, 50 –60 Hz |
|||
|
Dimensions |
140 x 235 x 56 mm |
|||
|
Weight |
2.5 kg with two lasers, 2.2 kg with one laser |
|||
BiologyVisualization of cellular components with minimum perturbation |
GeologyCharacterization of minerals, detection of components distribution and their phase transitions |
Material scienceInvestigation of various materials with high spatial resolution - superconductors, polymers, coatings, composites, carbon nanotubes, graphene, etc |
PharmaceuticsIdentification and distribution of chemical components and molecular conformers in various drugs |
CosmetologyA promising technique for researching the composition of skincare products as well as their penetration ability |
Heritage and Art, GemologyDetermination of pigments and binding agents used in painting Spectroscopic analysis of archaeological samples (ceramics, glass, etc.) gives information on their origins and history Rapid identification of precious and semi-precious stones, e.g. identification of natural and synthetic diamonds |
PolymersDetermination of polymers microstructure and composition, including qualitative analysis of copolymers, determination of additives and fillers (plasticizers, pigments, colorants, etc.) Kinetics research: polymerization, destruction processes (chemical or thermal) |
ForensicsIdentification of unknown substances, different types of fibers, glasses, paints, explosive materials, inks, narcotic and toxic substances, proof of authenticity of documents |